

You’re cleaning out your closet and stumble upon an old phone, a relic from a few years back. What do you do with it? Toss it in the trash? Or maybe leave it to gather dust? This scene might seem trivial, but it paints a picture of a much larger issue—the E-Waste Crisis.
Every electronic device we discard contributes to a growing environmental problem that affects our planet and our health. It’s time to delve into this pressing issue, exploring what it means and how we can work together to find effective, sustainable solutions.
The E-Waste Crisis is a pressing issue involving the disposal of electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, and appliances. These items, when discarded, are known as e-waste.
Such waste contains hazardous materials, including lead and mercury, which can seep into soil and water, posing environmental and health risks. The rapid growth of e-waste is fueled by technological advancements and changing consumer habits.
This situation calls for urgent action to implement sustainable recycling and responsible disposal methods, aiming to reduce the detrimental effects on both human health and the environment.
Effective solutions play a vital role in tackling various challenges, especially in today’s fast-paced world. They not only enhance productivity but also encourage creativity and flexibility. When businesses or communities adopt well-planned approaches, they can streamline operations, cut expenses, and boost overall efficiency.
Moreover, these solutions often lead to happier customers because they directly address their needs and worries.
Furthermore, effective solutions contribute significantly to a positive environment by encouraging individuals to take charge and work together to solve problems. This collaboration fosters a sense of responsibility and belonging among team members, leading to increased motivation and output.
Essentially, the importance of effective solutions lies in their capacity to create long-lasting benefits that support both the organization and its members in an ever-changing world. By focusing on practical and innovative strategies, we can ensure a brighter and more sustainable future for all.
Addressing the e-waste crisis is essential to safeguard our environment and communities. One primary concern is environmental protection. E-waste contains harmful materials that can seep into the soil and water, leading to contamination. By implementing effective recycling methods, we can reduce these risks and prevent landfills from overflowing.

Furthermore, the health of communities is at stake, especially in areas where informal recycling is common. Exposure to toxic substances from e-waste can result in severe health problems.
Resource conservation is another significant aspect. By retrieving valuable materials like gold and copper from e-waste, we lessen the need for extracting new resources, which in turn reduces environmental impact and production costs. This also supports a circular economy, where materials are reused rather than discarded.
Moreover, addressing e-waste presents economic opportunities by creating jobs in recycling and recovery sectors, thus benefiting local economies and promoting sustainable practices.
The e-waste crisis is a pressing global issue, exacerbated by rapid technological advancement and consumerism. As electronic devices become obsolete at an unprecedented rate, the disposal of these items poses significant environmental challenges.

E-waste contains hazardous materials that can leach into soil and water, contributing to pollution and health risks. Moreover, the sheer volume of e-waste generated—projected to reach 67 million tons by 2030—demands immediate and effective solutions. Below are ten impactful strategies that can help mitigate the e-waste crisis.
Design for Longevity (DfL) is a critical approach in product design that emphasizes creating items with an extended and optimal lifespan. This concept is essential for promoting sustainability and reducing waste, particularly in the context of a circular economy.
By focusing on the interplay between user needs, business viability, and resource efficiency, designers can enhance the durability and relevance of products throughout their lifecycle. Below are key aspects of Design for Longevity:
Promoting repairability is a vital strategy in enhancing product sustainability and consumer rights. This approach not only reduces waste but also empowers consumers by providing them with the ability to extend the life of their products.
By designing items that are easier to repair, manufacturers can foster brand loyalty and align with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices. Below are key aspects of promoting repairability:
Implementing recycling programs is essential for promoting environmental sustainability and reducing waste. Effective recycling initiatives not only divert materials from landfills but also foster a culture of responsibility among participants.
A well-structured program involves careful planning, education, and community engagement to ensure success. Below are key steps to consider when implementing a recycling program:
Encouraging reuse and donation is a powerful strategy for reducing waste and fostering community connections. By promoting the idea that items can have multiple lives, individuals and organizations can significantly lessen their environmental impact while helping those in need.
This approach not only conserves resources but also strengthens community bonds through shared experiences and mutual support. Here are effective ways to encourage reuse and donation:
Utilizing eco-friendly materials is a critical aspect of sustainable design and construction. These materials are sourced from renewable resources or recycled content, significantly reducing environmental impact during production, use, and disposal.
By choosing eco-friendly options, businesses and consumers can contribute to a healthier planet while also benefiting from energy efficiency and reduced costs. Below are key types of eco-friendly materials:
Fostering a circular economy is essential for creating sustainable production and consumption systems that minimize waste and promote resource efficiency. This economic model seeks to extend the lifecycle of products, ensuring that materials are reused, repaired, and recycled rather than discarded.
By shifting from a linear “take-make-dispose” approach to a circular one, businesses can reduce their environmental impact while creating economic opportunities. Here are key strategies for fostering a circular economy:
Advocating for policy changes is crucial for driving social, economic, and environmental improvements. Effective advocacy involves strategic planning, relationship building, and clear communication with policymakers and the public.
By mobilizing communities and leveraging data, advocates can influence decision-makers to adopt policies that reflect community needs and values. Here are key strategies for successful advocacy:
Promoting awareness campaigns is an effective strategy for educating the public about important issues, driving engagement, and inspiring action. These campaigns leverage various communication channels to reach target audiences and create a lasting impact.
By raising awareness, organizations can influence public perception, encourage community involvement, and advocate for policy changes. Here are essential steps to effectively promote awareness campaigns:
Implementing take-back schemes is a crucial strategy for promoting sustainability and reducing waste in various industries. These programs encourage consumers to return products at the end of their life cycle, allowing manufacturers to recycle or repurpose materials, thus contributing to a circular economy.
By fostering responsible consumption and enhancing recycling efforts, take-back schemes can significantly mitigate environmental impacts. Here are key components of effective take-back schemes:
Supporting innovative technologies is vital for advancing sustainability and addressing environmental challenges. These technologies encompass a wide range of applications, from renewable energy solutions to efficient waste management systems.
By investing in and promoting these innovations, we can foster economic growth while mitigating climate change impacts. Here are key areas where innovative technologies are making a significant difference:
By implementing these solutions, stakeholders from manufacturers to consumers can collectively address the growing e-waste crisis, promoting sustainability while protecting our environment.
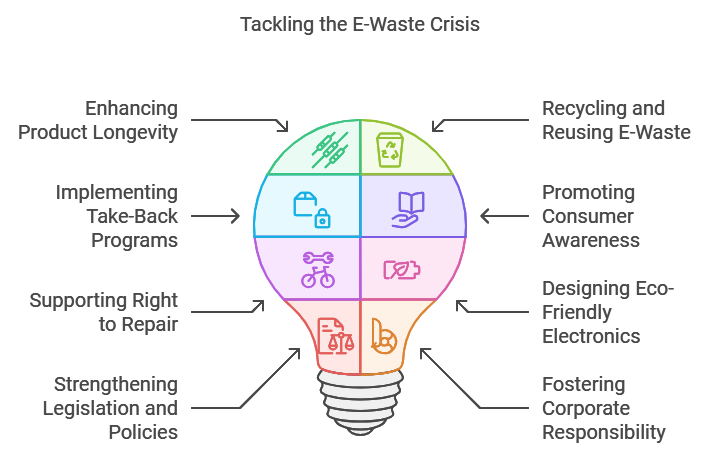
Addressing the E-Waste Crisis is more crucial than ever. It requires collective efforts from individuals, corporations, and governments to implement effective solutions. By enhancing product longevity, recycling, and supporting right-to-repair initiatives, we can significantly reduce electronic waste.
Designing eco-friendly electronics and promoting consumer awareness are key steps toward a sustainable future. Strengthening legislation and fostering corporate responsibility will pave the way for a cleaner environment. As we move forward, it’s essential to continuously strive for innovative approaches to tackle this pressing issue.
If you found this article helpful, explore more insightful content on our website to stay informed and empowered!
